Abstract
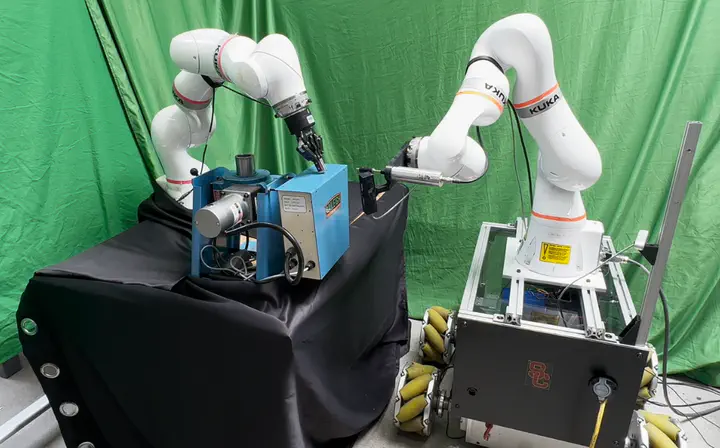
Screw-driving is an important operation in numerous applications. In many situations, hole pose cannot be estimated very accurately. Autonomous screw-driving cannot be performed by traditional industrial manipulators in position control mode when the hole pose uncertainty is high. This paper presents a mobile manipulator system for performing autonomous screw-driving in the presence of uncertainties in the hole estimates. It utilizes active compliance in the form of impedance control of the robot and passive compliance in the screwing driving tool to deal with uncertainties. We present a physics-informed machine learning approach to automatically characterize the motion of the screw tip and explain how this motion leads to successful operation in the presence of uncertainty. We also present an approach for detecting failure modes and taking corrective actions. Code and video is available at:https://sites.google.com/usc.edu/physicsinformedscrewdriving